When talking about automotive components, understanding the role and function of individual parts is essential. In the world of mechanics, the crankshaft and transmission stand as two of the most vital components. They are, however, distinct from each other. Let’s delve into the specifics of these two critical components, beginning with the crankshaft, then leading to the transmission, and finally, discussing their interrelation.
The crankshaft is an integral part of an internal combustion engine. It serves to convert the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is then transferred to the wheels of the vehicle via the transmission. The crankshaft, made of high-strength alloy steel, must withstand the immense forces exerted by the pistons, and thus it is constructed for durability and performance. Its shape is cylindrical with multiple “crankpins,” or bearing surfaces, which interact with the pistons.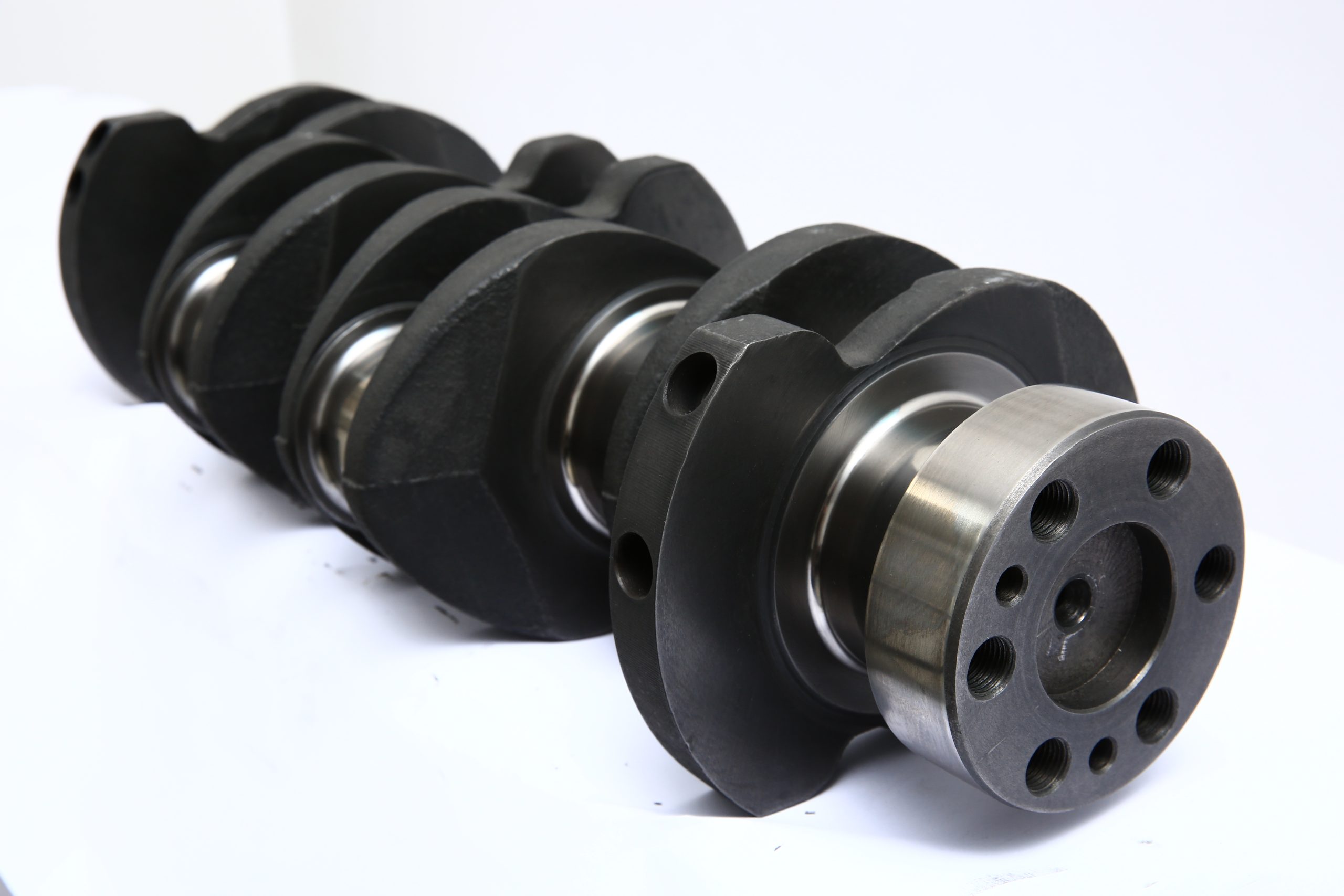
On the other hand, the transmission serves as the link between the engine and the drive wheels. It uses gears and a clutch to convert the engine’s output into torque that can move the vehicle. The transmission can be manual or automatic, with the former requiring the driver to manually shift gears, and the latter automatically adjusting the gear ratios as the vehicle moves.
Though the crankshaft and transmission are separate components, they do have a vital connection. The engine’s crankshaft is connected to the transmission via the clutch in manual vehicles, or the torque converter in automatic vehicles. This connection allows the rotational motion generated by the crankshaft to be transmitted to the wheels.
The crankshaft’s role is to generate rotational motion, while the transmission’s function is to control and transmit this power to the wheels. The crankshaft, therefore, is not part of the transmission but indeed is its key partner. Without the crankshaft’s generated power, the transmission would have nothing to transmit, and without the transmission, the power from the crankshaft would not reach the wheels.
In conclusion, the crankshaft is not a part of the transmission; rather, they work together to ensure the operation of the vehicle. They form a symbiotic relationship, with the crankshaft converting the linear motion into rotational motion, and the transmission taking this rotational motion and converting it into a force that can move the vehicle. While they are separate components, their roles are interconnected, making them both essential to the proper functioning of any motor vehicle.
Is the Crankshaft Part of the Transmission?
1. Understanding the Crankshaft
The crankshaft is a key component of an internal combustion engine. Its primary function is to transform the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which powers the vehicle. The crankshaft is connected to the pistons via the connecting rods, which move up and down as the cylinders in the engine fire.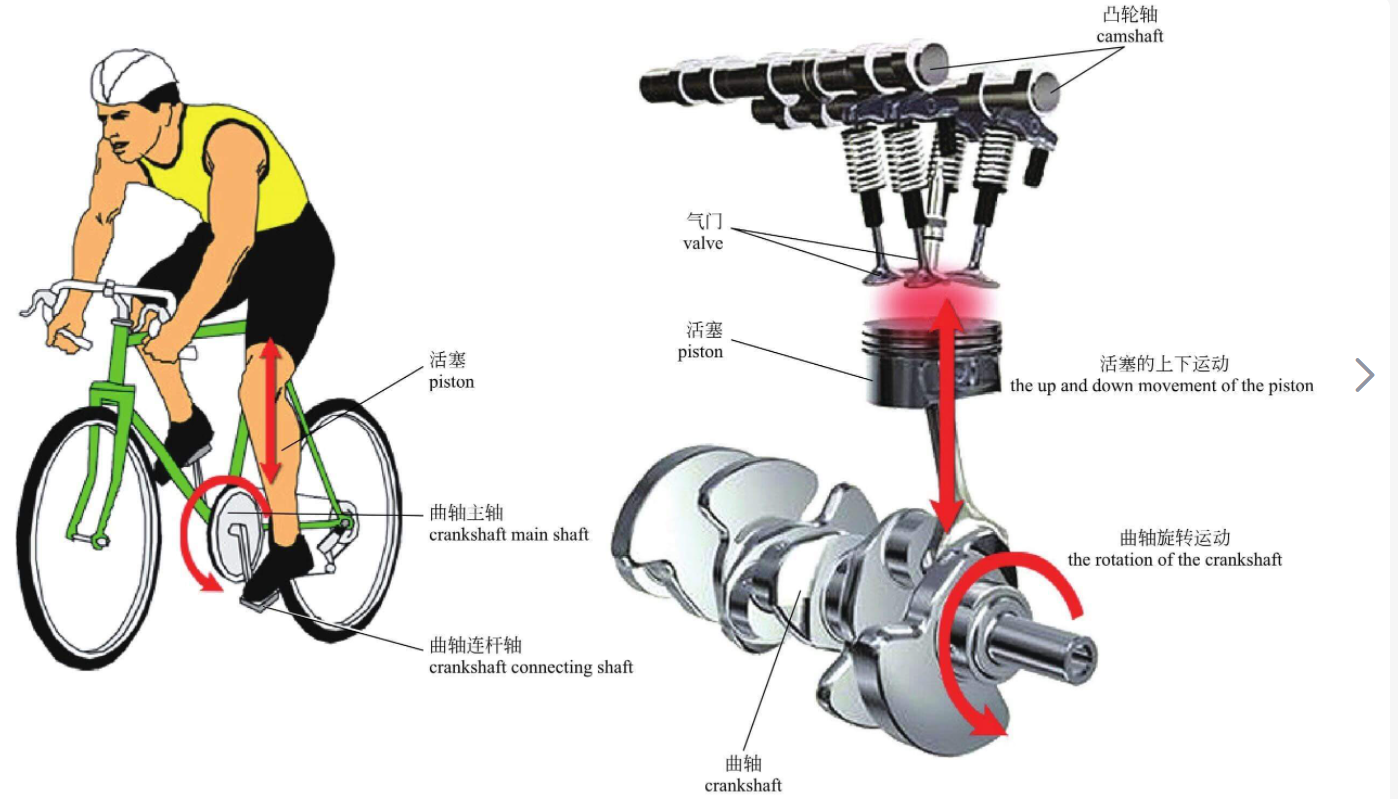
2. Defining the Transmission
The transmission, on the other hand, is a separate component that is responsible for distributing power generated by the engine to the wheels of the vehicle. It does this by shifting gears to adjust the speed and torque in a way that is most efficient for the current driving conditions.
3. The Relationship Between the Crankshaft and the Transmission
While the crankshaft and the transmission are separate components, they are closely related and work together to move the vehicle. The rotational motion generated by the crankshaft is transferred to the transmission, which then uses this energy to rotate the wheels of the vehicle.
4. Transmission Components: The Flywheel and Clutch
Between the engine (where the crankshaft is located) and the transmission are important components like the flywheel and the clutch (or torque converter in automatic transmissions). The flywheel, connected to the crankshaft, helps to smooth out the power delivery from the engine. The clutch or torque converter, when engaged, transfers the rotation of the flywheel to the transmission.
5. No, the Crankshaft is Not Part of the Transmission
To answer the question directly, the crankshaft is not a part of the transmission. While it plays a crucial role in transmitting the engine’s power to the transmission, it is a distinct component that is part of the engine, not the transmission.
6. Importance of Regular Maintenance
Both the crankshaft and the transmission are vital to the vehicle’s operation, and both require regular maintenance to ensure they function properly. For the crankshaft, this might include regular oil changes to ensure it remains lubricated. For the transmission, regular fluid checks and changes are crucial to its operation and longevity.
7. Signs of Crankshaft Problems
Crankshaft problems can lead to serious issues with your vehicle’s engine. Some of the signs that your crankshaft may be experiencing problems include unusual noises, excessive vibrations, and poor engine performance. In some cases, the vehicle might not start at all. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a professional.
8. Signs of Transmission Problems
Just as with the crankshaft, there are certain signs that might indicate a problem with your transmission. These include difficulty in shifting gears, unusual noises, a burning smell, and leaking transmission fluid. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should have your vehicle checked by a professional as soon as possible.
9. Crankshaft and Transmission Repairs
If there is a problem with your crankshaft or transmission, it’s important to get it repaired as soon as possible. Depending on the problem, this could involve replacing the affected part, or it could require more extensive repairs. It’s always best to consult with a qualified mechanic to determine the best course of action.
10. Preventive Measures
Preventive maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s crankshaft and transmission. This includes regular oil changes, using the correct type of transmission fluid, and avoiding harsh driving habits. By taking care of your vehicle, you can prevent costly repairs and extend the life of your engine and transmission.
11. Understanding the Entire Drivetrain
The crankshaft and the transmission are part of the larger drivetrain system, which also includes the axles and the wheels. Understanding how all these components work together can help you maintain your vehicle better and identify potential problems before they become serious.
12. Concluding Thoughts
While the crankshaft is not a part of the transmission, it plays a vital role in transmitting power from the engine to the transmission. Regular maintenance and prompt repairs can help ensure that both these components continue to function properly, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of your vehicle.