The crankshaft, a critical component in the engine, plays a vital role in converting reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation. Its production process, therefore, involves a series of intricate steps to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
At the heart of the crankshaft production process lies the forging step. This is where raw metal is heated to a specific temperature and hammered into the preliminary shape of the crankshaft. The process is performed under extreme pressure to ensure the integrity and strength of the material.
Heat treatment follows forging. This process improves the hardness and toughness of the crankshaft, thereby enhancing its resistance to wear and tear. The crankshaft is heated and rapidly cooled under controlled conditions. This process is often referred to as quenching. After quenching, the crankshaft undergoes a tempering process to reduce the brittleness caused by quenching.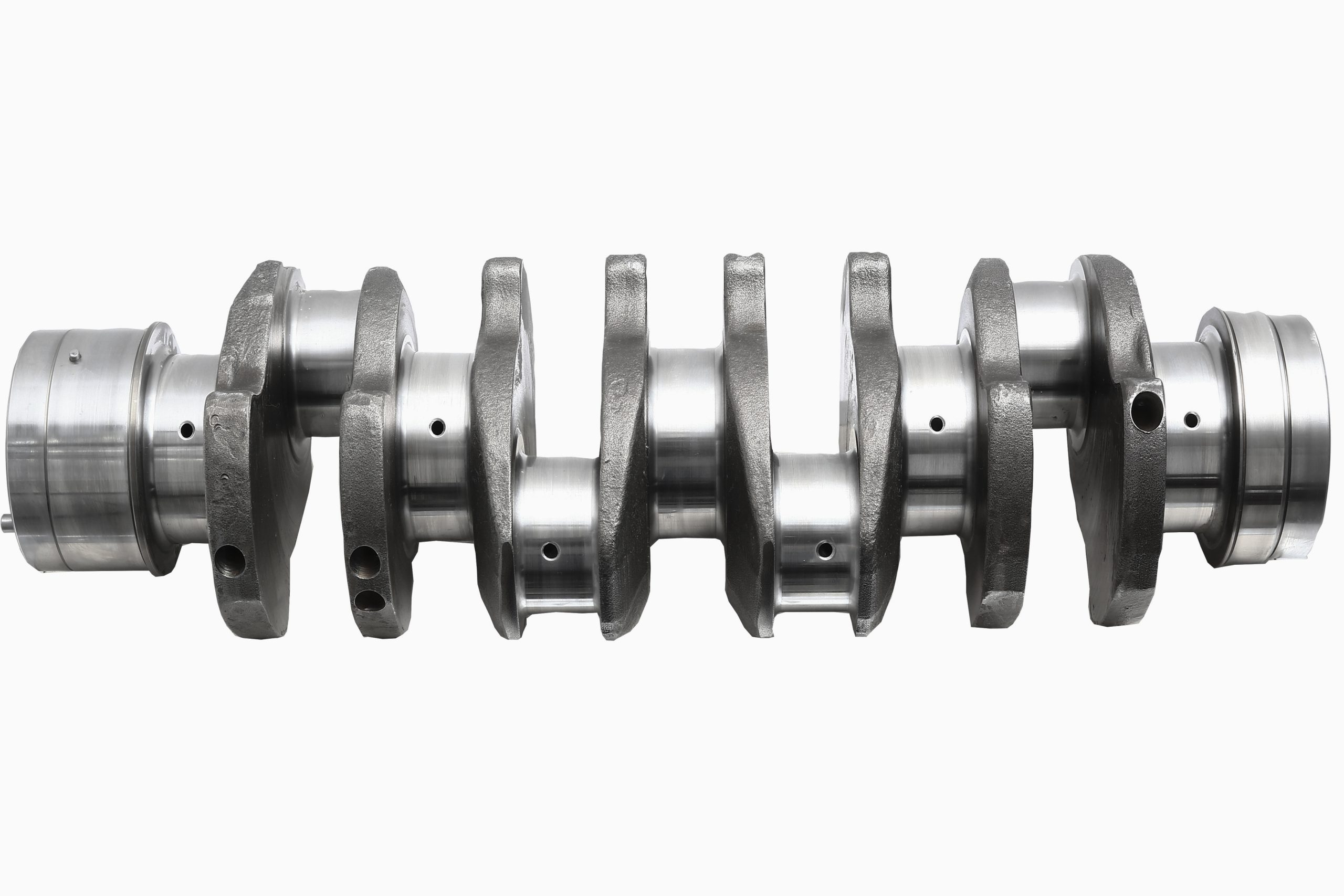
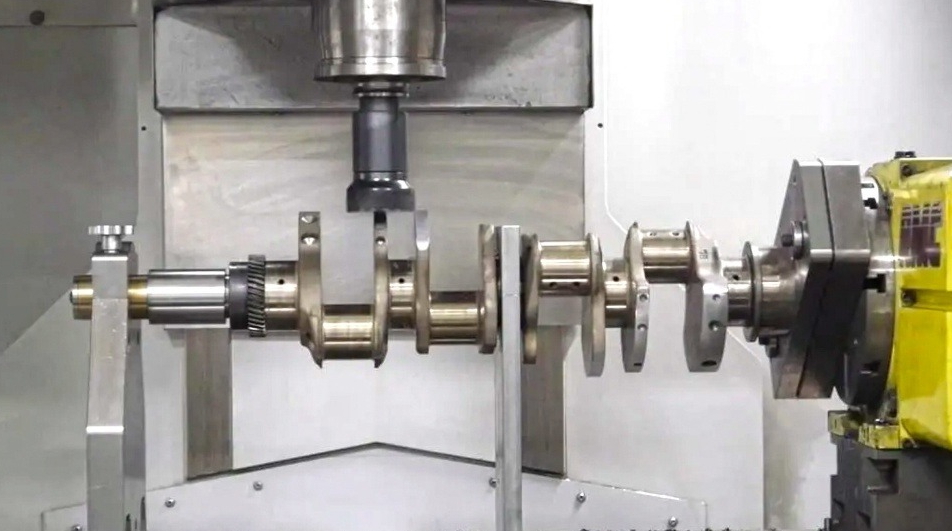
Machining is the next step, where the crankshaft is shaped and sized according to precise specifications. This involves grinding, milling, and drilling to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. Each crankshaft pin and main journal are accurately ground to ensure they are perfectly round and have the correct diameter.
Inspection is a crucial phase in the crankshaft production process. Here, each crankshaft undergoes a series of checks to verify its dimensions, balance, and surface finish. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic and magnetic particle inspection, are often used to detect any internal or surface defects.
Quality assurance is the final step in the production process. The crankshaft is subject to rigorous testing and inspection to confirm it meets all specifications and standards. This includes dimensional checks, hardness tests, and performance trials.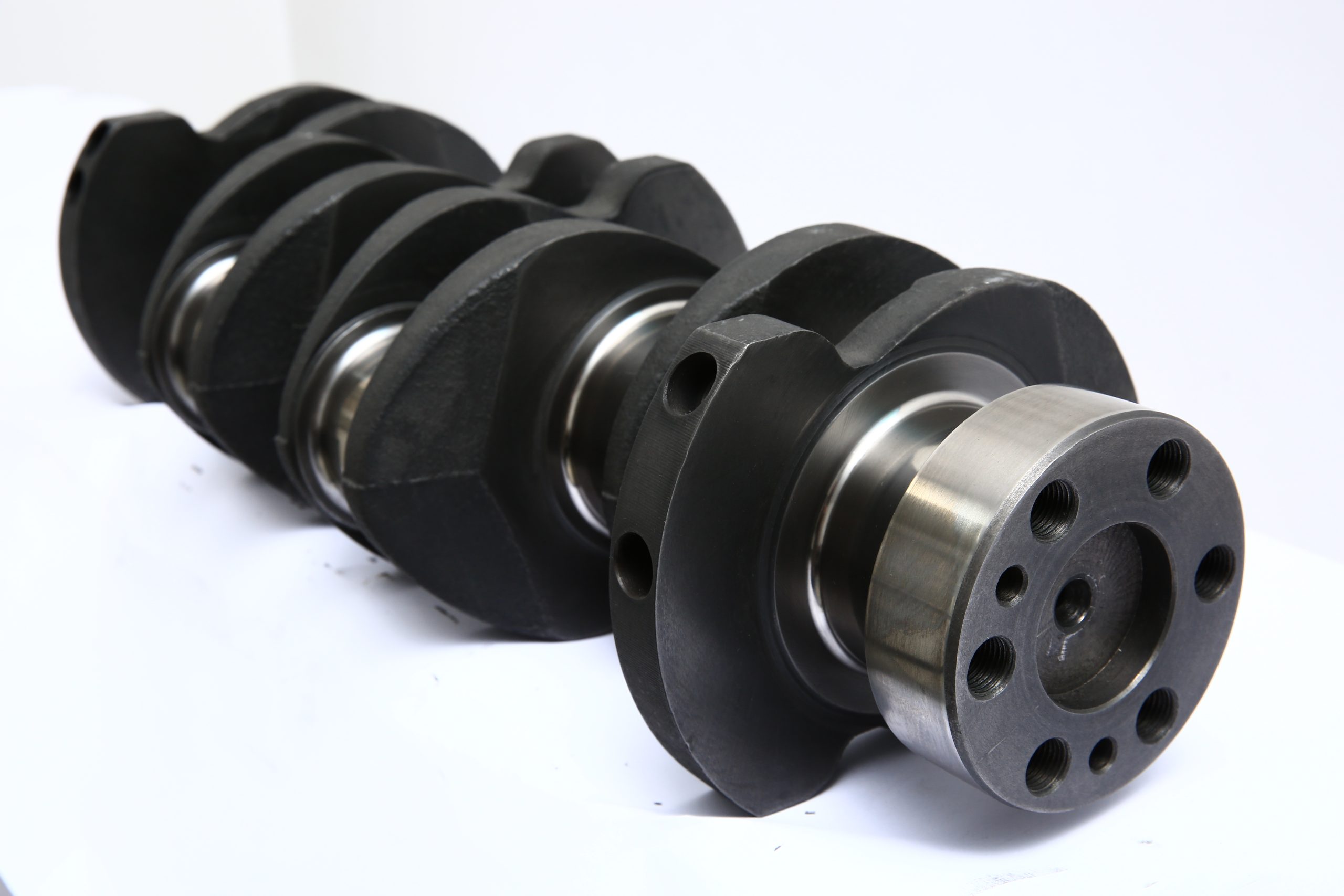
The advancements in technology have significantly transformed the crankshaft production process. The adoption of computer numerical control (CNC) machining, for example, has allowed for higher precision and efficiency. Moreover, the development of high-performance materials and coating technologies has enhanced the crankshaft’s durability and performance.
In conclusion, the production of a crankshaft is a complex process that demands precision and expertise. It involves various stages, each of which plays a critical role in ensuring the final product meets the stringent quality and performance requirements. With ongoing technological advancements, the process continues to evolve, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable production methods.
Introduction
This section provides a brief overview of the importance of the crankshaft in engine operation and introduces the complex process of its production.
The Forging Process
This part delves into the initial stage of crankshaft production, where raw metal undergoes forging to form the initial shape of the crankshaft, ensuring material integrity and strength.
Heat Treatment
This segment discusses the subsequent stage of heat treatment, a crucial process that enhances the hardness, toughness, and wear resistance of the crankshaft through controlled heating and cooling.
Machining
In this section, we explore the machining process, where the crankshaft is further shaped and sized according to precise specifications, including grinding, milling, and drilling operations.
Inspection
This part sheds light on the critical inspection phase, where each crankshaft undergoes a series of checks to verify dimensions, balance, and surface finish, with an emphasis on non-destructive testing methods.
Quality Assurance
This segment examines the final phase of the crankshaft production process, focusing on the rigorous testing and inspection conducted to ensure the product meets all specifications and standards.
Technological Advancements
This section offers insight into the recent technological advancements in the crankshaft production process, such as the adoption of CNC machining and the development of high-performance materials and coatings.
Conclusion
The conclusion encapsulates the complex and precision-demanding process of crankshaft production and anticipates future trends in the field, influenced by ongoing technological advancements.