Common causes for crankshaft sensor failure include wear and tear over time, exposure to heat and vibrations, oil or dirt contamination, and faulty electrical connections or damaged wiring.
Introduction
In this article, we delve into the world of automotive mechanics, specifically focusing on the crankshaft sensor, a crucial component of a modern vehicle’s engine management system.
Definition of a Crankshaft Sensor
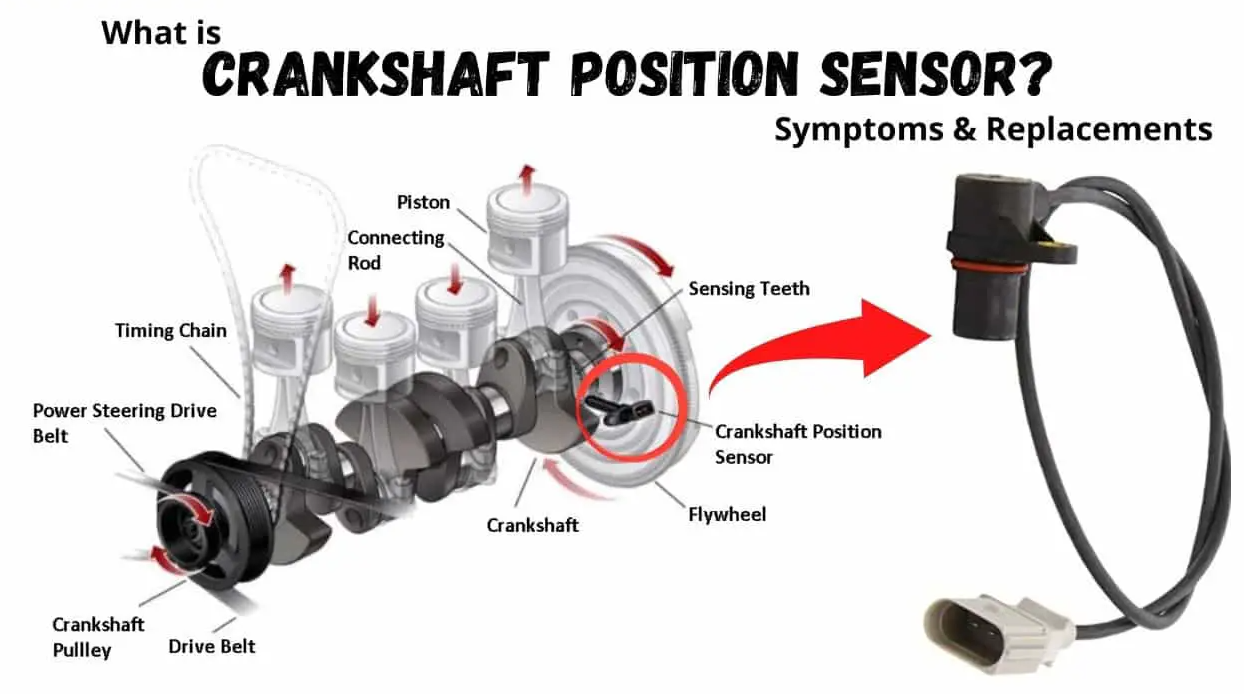
The crankshaft sensor, often abbreviated as the crank sensor, is a device installed in an internal combustion engine to monitor the position or rotational speed (RPM) of the crankshaft. This information is necessary for the engine control unit (ECU) to balance fuel injection, ignition timing, and other engine functions.
The Role and Importance of a Crankshaft Sensor in a Vehicle
The crankshaft sensor plays a pivotal role in the overall functioning of a vehicle. As an integral part of the engine management system, it provides vital data to the ECU. With the information gathered from the crankshaft sensor, the ECU can adjust parameters such as fuel injection timing and ignition timing to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Without a properly functioning crankshaft sensor, the vehicle might experience a range of problems including poor performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and even engine misfires or stalling. In the worst-case scenario, the vehicle might not start at all.
In the sections that follow, we will delve deeper into the operational aspects of a crankshaft sensor, the common problems it may encounter, and what causes these issues.
Basics of a Crankshaft Sensor Operation
In this section, we will demystify the operation of the crankshaft sensor, highlighting its basic functional principles and key components.
How a Crankshaft Sensor Works
The crankshaft sensor operates based on electromagnetic induction. It consists of a magnet surrounded by a coil of wire, positioned close to the metallic teeth on the crankshaft. As the crankshaft rotates, these teeth pass by the sensor, causing a change in the magnetic field. This change generates a voltage signal in the coil, which changes with the rotational speed of the crankshaft.
The resulting signal is sent to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which interprets it as a series of high and low voltages. The ECU then calculates the position and speed of the crankshaft from these voltages.
This vital information allows the ECU to control fuel injection, ignition timing, and other engine operations. This ensures the engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal emissions.
Components of a Crankshaft Sensor
A crankshaft sensor is a fairly simple yet ingenious device comprising of several key components:
- Magnet: The core component which interacts with the metallic teeth of the crankshaft, creating a change in magnetic field with each passing tooth.
- Coil: This wraps around the magnet. The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the coil.
- Housing: A protective casing that shelters the magnet and coil from the harsh operating environment of an engine.
- Wiring and connector: These facilitate the transmission of the generated signal to the ECU.
These components work together to convert mechanical motion into an electrical signal that the ECU can understand and utilize.
Common Problems with Crankshaft Sensors
Even the best-designed systems can encounter issues, and the crankshaft sensor in a vehicle is no exception. Let’s delve into the common problems associated with crankshaft sensors and how to identify them.
Symptoms of a Bad Crankshaft Sensor
A crankshaft sensor that’s failing or has gone bad can present several symptoms. Recognizing these can help identify a crankshaft sensor problem early on:
- Engine Misfires or Stalling: The engine may sputter or cut out without warning, potentially even while the vehicle is in motion. This happens when the ECU doesn’t receive accurate information about the crankshaft position and disrupts the firing sequence.
- Difficulty Starting the Car: Without correct data from the crankshaft sensor, the ECU cannot adjust fuel injection and ignition timing correctly, making it harder for the engine to start.
- Poor Acceleration: When the crankshaft sensor malfunctions, the ECU may misinterpret crankshaft speed, leading to suboptimal engine timing and poor acceleration.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: Incorrect fuel injection timing caused by a faulty crankshaft sensor can result in decreased fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: If the ECU detects an issue with the crankshaft sensor, it will often trigger the check engine light on the dashboard.
How to Diagnose a Failing Crankshaft Sensor
Diagnosing a faulty crankshaft sensor typically involves a few steps:
- Error Code Reading: The first step is usually to use an OBD-II scanner to read the engine error codes. This can help identify if the problem is related to the crankshaft sensor.
- Visual Inspection: Checking the crankshaft sensor and its connections for obvious signs of damage or contamination can be informative. Look for things like broken wires, corrosion, or oil leakage.
- Multimeter Testing: In some cases, a multimeter can be used to test the resistance and voltage of the crankshaft sensor. However, this requires some technical knowledge and the specific resistance and voltage ranges for your vehicle’s sensor.
Remember, if you’re not comfortable diagnosing the problem yourself, it’s always a good idea to bring your vehicle to a professional mechanic.

What Causes a Crankshaft Sensor to Go Bad?
Understanding the common reasons for crankshaft sensor failure can help in early diagnosis and prevention of serious engine problems. Let’s look at these causes in more detail.
Wear and Tear Over Time
Like all mechanical components, crankshaft sensors are subject to wear and tear over time. Prolonged use can cause internal components of the sensor, like the magnet or coil, to degrade and become less effective at generating a clear signal. This can eventually lead to sensor failure.
Heat and Vibrations
Located in the harsh environment of the engine bay, crankshaft sensors are continuously exposed to heat and vibrations from the engine. Over time, this can lead to mechanical stress and deterioration of the sensor components, ultimately causing them to fail.
Oil or Dirt Contamination
Contamination of the crankshaft sensor by engine oil, dirt, or other debris can also lead to problems. Contaminants can interfere with the sensor’s ability to generate an accurate signal, leading to erratic readings or even complete failure.
Faulty Connections or Damaged Wiring
Faulty electrical connections or damaged wiring can prevent the crankshaft sensor’s signal from reaching the Engine Control Unit (ECU). This can be due to corrosion, wear and tear, or physical damage to the wiring or connectors.
Consequences of a Bad Crankshaft Sensor
A failing or malfunctioning crankshaft sensor can lead to a variety of problems, impacting everything from engine performance to vehicle safety. Let’s explore these consequences further.
Impact on Engine Performance
One of the primary roles of the crankshaft sensor is to provide data for optimal engine timing. If the sensor is not working properly, the engine’s timing may be off, leading to performance issues such as:
- Difficulty starting the vehicle
- Reduced power and acceleration
- Engine stalling or misfiring
- Unstable idling or engine vibration
These issues can significantly affect the driving experience and the overall reliability of your vehicle.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Incorrect data from a faulty crankshaft sensor can lead to suboptimal fuel injection timing. This often results in the engine burning more fuel than necessary, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. Over time, this can result in higher fuel costs and increased emissions, contributing to environmental pollution.
Safety Concerns
Finally, a malfunctioning crankshaft sensor can pose significant safety risks. If the engine stalls while the vehicle is in motion, it could lead to loss of control and increase the risk of an accident. Similarly, difficulties starting the vehicle can leave you stranded in potentially unsafe locations or situations.
Fixing a Bad Crankshaft Sensor
Repairing or replacing a faulty crankshaft sensor is essential to restore optimal vehicle performance and safety. Let’s take a closer look at the steps involved.
When to Consider Sensor Replacement
Replacing the crankshaft sensor is usually the recommended course of action when:
- The engine is showing symptoms of a bad crankshaft sensor such as stalling, difficulty starting, or decreased performance.
- The vehicle’s OBD-II scanner indicates an error code related to the crankshaft sensor.
- A professional mechanic has inspected the vehicle and confirmed the sensor to be the source of the problem.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Crankshaft Sensor
Here is a general guide to replacing a crankshaft sensor:
- Locate the Sensor: The crankshaft sensor is usually located near the engine crankshaft. Its exact location can vary depending on the vehicle model, so consult your vehicle manual or a trusted mechanic if unsure.
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Before starting, disconnect the negative terminal of the car battery for safety.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Unplug the electrical connector from the sensor, then unscrew and remove the old sensor from its mount.
- Install the New Sensor: Position the new sensor in the mount and secure it with the screws. Then, reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the Battery and Test: Reconnect the battery, start the car, and observe for any continuing issues or error codes.
Please note, while this process may seem straightforward, it can be more complicated in practice due to the sensor’s location or other factors. Always consider seeking professional assistance if you’re unsure.
Can a Bad Crankshaft Sensor be Repaired?
Generally, crankshaft sensors are not repairable and need to be replaced when they fail. They are sealed units and their internal parts are not typically accessible for repair. Furthermore, due to their relative affordability, it is often more cost-effective and reliable to replace a bad sensor than attempting a repair.
Preventing Crankshaft Sensor Issues
While a crankshaft sensor can’t last forever, there are ways to prolong its lifespan and prevent premature failure. Below, we will discuss the importance of regular maintenance and paying attention to early warning signs.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance
One of the best ways to prevent issues with the crankshaft sensor is through regular vehicle maintenance. Here are some tips:
- Regular Oil Changes: Changing your vehicle’s oil at the recommended intervals can help keep the crankshaft sensor clean and functioning properly. This can prevent oil contamination, which is a common cause of sensor failure.
- Scheduled Inspections: During routine vehicle inspections, request that your mechanic checks the condition of the crankshaft sensor. They can look for signs of wear, damage, or contamination and clean or replace the sensor as needed.
- Proper Cleaning: If your vehicle operates in dirty or dusty conditions, it may be worth regularly cleaning the crankshaft sensor area to prevent contamination.
Paying Attention to the Early Signs
Recognizing the early signs of a failing crankshaft sensor can help you prevent further damage. If your vehicle shows any symptoms such as difficulty starting, poor performance, reduced fuel efficiency, or an illuminated check engine light, it’s important to have it checked by a professional as soon as possible. Ignoring these signs may lead to more serious engine problems down the line.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, the role of the crankshaft sensor is crucial in the functioning and performance of a vehicle. Let’s recap what we’ve learned and reflect on the importance of proactive maintenance.
Recap of Crankshaft Sensor Problems and Solutions
We’ve explored the various issues that can plague a crankshaft sensor, such as wear and tear, heat and vibrations, contamination, and faulty connections. We also discussed the symptoms of a failing sensor, its impacts on engine performance, fuel efficiency, and safety. In terms of solutions, we’ve outlined the signs that indicate when replacement is necessary, provided a guide to replacing a crankshaft sensor, and highlighted the importance of preventive measures such as regular vehicle maintenance and early symptom detection.
Throughout this article, we hope to have stressed the importance of promptly addressing crankshaft sensor problems and the crucial role high-quality components play in a vehicle’s operation. For example, using reliable parts from trusted brands like FEDA can help ensure the longevity and performance of components like the crankshaft sensor.
Final Thoughts
Taking care of a vehicle’s engine is more than just an investment in the vehicle itself—it’s an investment in safety, performance, and peace of mind. The humble crankshaft sensor is a great example of a small component with a large role. By understanding its function, identifying the signs of failure, and taking proactive steps to maintain and replace it as needed, vehicle owners can enjoy smoother drives, safer journeys, and less unexpected visits to the mechanic.