Connecting rods are fundamental components in internal combustion engines, playing an essential role in transferring force from the piston to the crankshaft, hence creating rotation. The length of a connecting rod can significantly influence an engine’s performance, affecting factors like piston speed, cylinder filling, and fuel efficiency.
Impact on Piston Speed
A longer connecting rod changes the speed of the piston in the cylinder. It reduces the piston speed around top dead center (TDC) and bottom dead center (BDC). This effect reduces the strain on the piston and rings, prolonging the life of these components and potentially the entire engine. A slower piston speed also allows more time for the fuel-air mixture to enter and exit the cylinder, improving cylinder filling and emptying.
Improvement in Cylinder Filling
Longer connecting rods provide a larger dwell period – the time during which the piston remains at or near TDC or BDC. This longer dwell period allows more time for the air-fuel mixture to enter the cylinder on the intake stroke, which can potentially improve cylinder filling. This advantage becomes significant at higher engine speeds where filling time is limited, potentially increasing power output.
Influence on the Combustion Process
Connecting rods of greater length have the advantage of reducing the piston speed around TDC, which can improve combustion efficiency. With slower piston speeds around TDC, there is more time for the air-fuel mixture to combust, leading to a more complete burn. This improved combustion efficiency could translate to better fuel efficiency and potentially lower emissions.
Less Side Load on the Piston
Longer connecting rods also result in less side load on the piston due to a reduced rod angularity. The reduced side loading can reduce friction between the piston and the cylinder wall, leading to a potential reduction in wear and tear, and thus, longer engine life.
Smoother Operation
Engines with longer connecting rods usually have smoother operation, due to the decreased piston speed and lesser side loads on the piston. This benefit can lead to less vibration and noise, enhancing the overall driving experience.
Limitations
Despite the many benefits, it’s important to note that there are practical limitations to the length of a connecting rod. A very long connecting rod might interfere with other engine components, or it may not fit within the engine block. Furthermore, a longer connecting rod is generally heavier, which could offset some of the benefits mentioned above. Therefore, the optimal length of a connecting rod is usually a compromise between these benefits and constraints.
To sum up, while the effects of longer connecting rods on engine performance can be quite complex, they generally offer multiple potential benefits, including improved cylinder filling, better combustion efficiency, reduced wear and tear, and smoother engine operation. All these factors make the case for why longer connecting rods can be better.
Contents
- Visual Inspection
- Straightness Check
- Crack Detection
- Measurement of Dimensions
- Weight Balancing
- Bolt Stretch and Torque Check
1. Visual Inspection
The first step in checking a connecting rod is a visual inspection. Look for obvious signs of damage such as cracks, deep scoring, or excessive wear in the area around the piston pin and crankshaft journals. Examine the rod bolts for any stretching or thread damage.
2. Straightness Check
To ensure proper engine operation, connecting rods must be straight. You can use a straight edge and feeler gauge to check the connecting rod’s straightness. Place the straight edge along the length of the rod and use the feeler gauge to check for gaps. Any deviation from straightness could lead to potential engine problems.
3. Crack Detection
Cracks can be a sign of serious issues in connecting rods. While some cracks may be visible to the naked eye, others may require a magnaflux test or a dye penetrant inspection. These methods can detect even small, invisible cracks, ensuring that the connecting rod is still in good condition.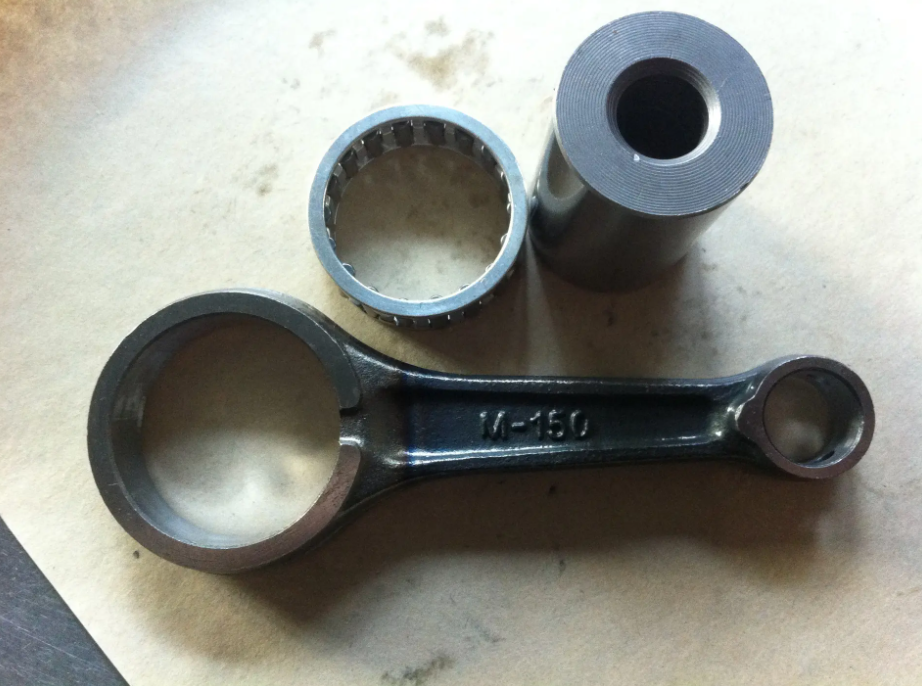
4. Measurement of Dimensions
Precise measurements of the connecting rod’s dimensions are critical. Use calipers or micrometers to measure the diameter of the big end (crankshaft side) and small end (piston side). Also, measure the overall length of the connecting rod. Compare your measurements with the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that the connecting rod is not deformed and is within tolerances.
5. Weight Balancing
Balancing is crucial in the connecting rod to maintain a smooth-running engine. Use a specialized connecting rod scale to measure the weight of the rod. It’s important to measure both the overall weight and the weight of each end separately. Any imbalance can lead to vibration, increased wear, and potentially, engine failure.
6. Bolt Stretch and Torque Check
Lastly, the bolt stretch and torque should be checked. This ensures the connecting rod bolts are not overly stretched or torqued, which could lead to failure. You can use a bolt stretch gauge and a torque wrench for this purpose. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s specifications when performing this check.
In conclusion, checking a connecting rod involves a thorough visual inspection, straightness check, crack detection, precise measurement of dimensions, weight balancing, and a bolt stretch and torque check. Through these steps, you can ensure that your connecting rod is in good shape and ready for efficient engine operation.