Rod Bearing is a critical component of an internal combustion engine that allows the connecting rods to rotate freely around the crankshaft.
It is designed to reduce friction and dissipate heat, contributing to smooth engine operation and prolonging the lifespan of the engine.
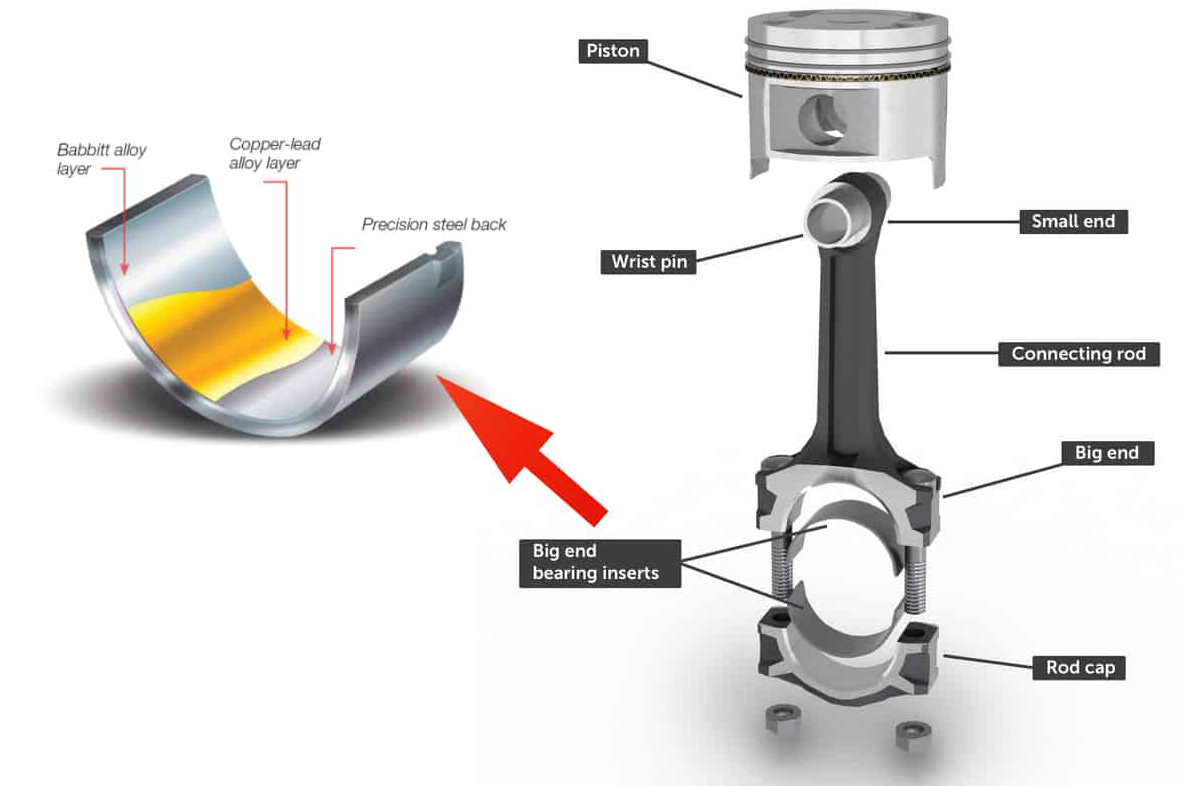
Composed of a strong steel shell and a softer inner lining material, rod bearings perform a delicate balancing act of strength and cushioning to ensure efficient energy transfer within the engine.
Introduction
The internal combustion engine is a complex machine with numerous parts working in harmony to convert fuel into mechanical energy. One of these integral parts is the rod bearing, an often overlooked yet crucial component for the engine’s operation.
Definition of a Rod Bearing
Its primary function is to hold the connecting rod in place, allowing it to rotate at the crankshaft and enabling the transfer of forces from the piston to the crankshaft.
Rod bearings are typically circular or semi-circular and constructed of durable metal materials, designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures inside the engine.
Purpose of a Rod Bearing
The rod bearing’s main purpose is to provide a point of connection between the piston’s connecting rod and the engine’s crankshaft.
Rod bearings also play a crucial role in lubricating the system.
Components and Types of Rod Bearings
Understanding the components and the different types of rod bearings can provide better insights into their functionality and importance in an internal combustion engine.
Material Composition
This lining material can be made from various alloys, such as babbitt metal, bronze, or a combination of aluminium, copper, and tin. This layer is vital as it reduces the friction between the bearing and the crankshaft, thus increasing the overall efficiency and lifespan of the engine.
The choice of material for rod bearings can significantly impact the engine’s performance, durability, and fuel efficiency.
Different Types of Rod Bearings
- Full or Flanged Bearings: These bearings are fully circular and cover the entire circumference of the crankshaft.
- Semi-circular or Half Bearings: These are the most common type of rod bearings found in most modern engines. They come in two halves, allowing for easier installation and replacement.
The type of rod bearing chosen for a particular application largely depends on the engine’s design and the specific performance requirements.
The Role of Rod Bearings in Engine Function
Rod bearings play a pivotal role in the overall function of an engine. They interact closely with several other components, with the most significant being the crankshaft.
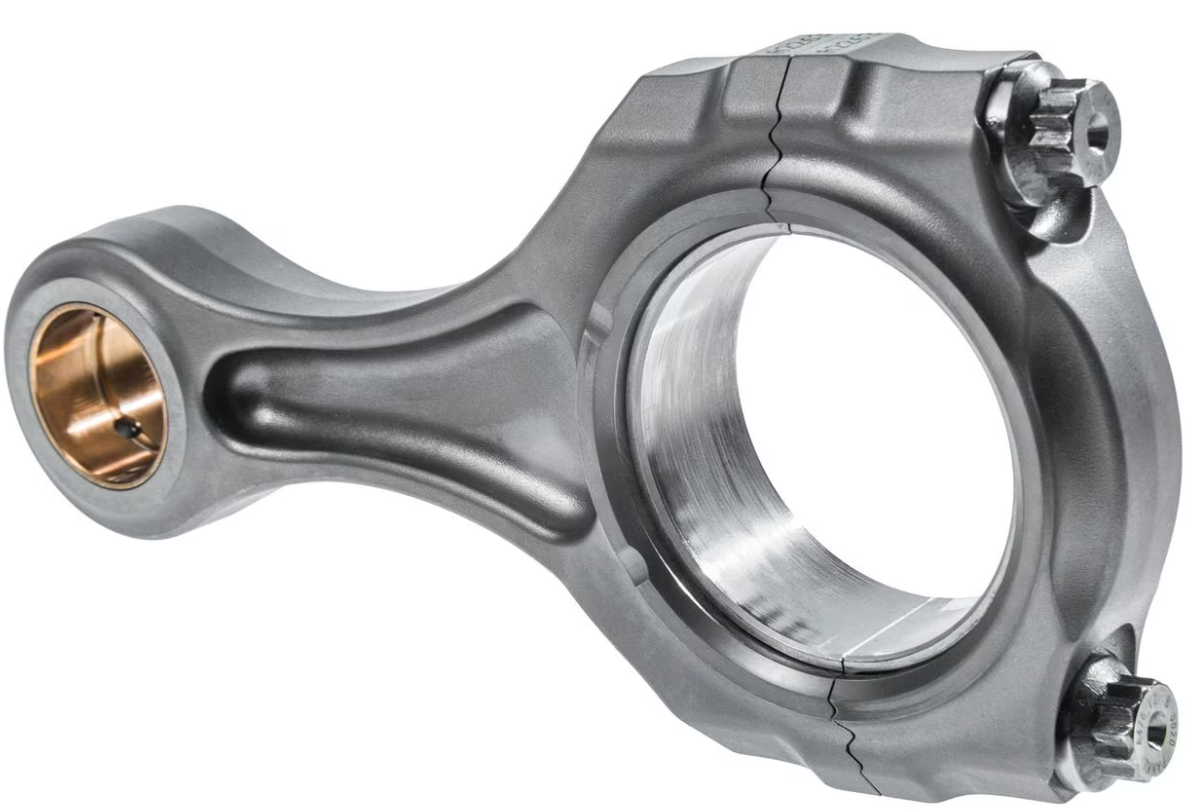

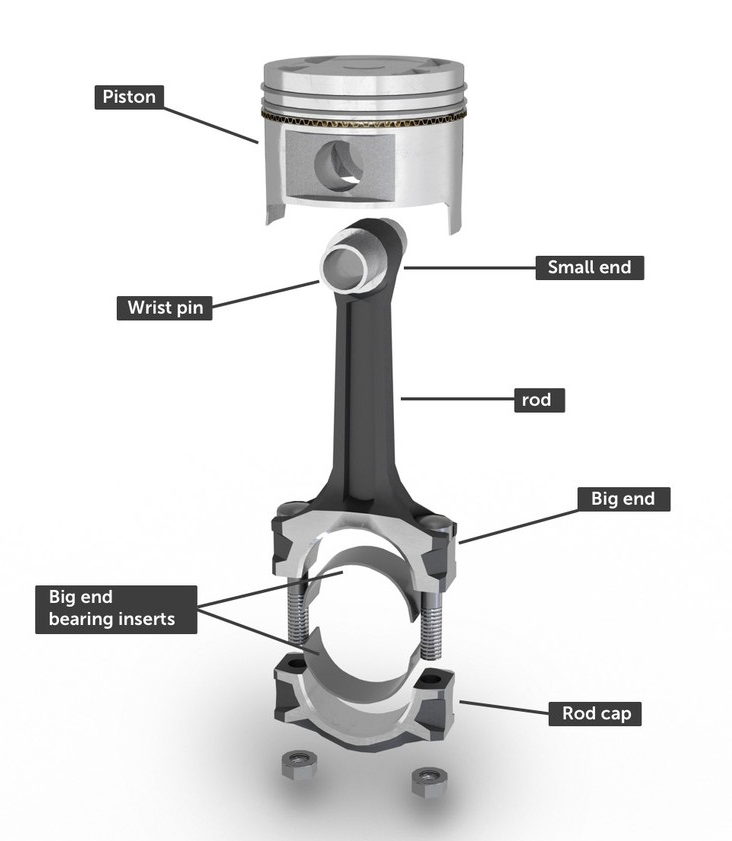
The Connection Between Rod Bearings and Crankshaft
The crankshaft and rod bearings share a dynamic relationship, with the rod bearings allowing the connecting rods to rotate freely around the crankshaft. This movement transforms the linear motion from the pistons into a rotational motion used to power the vehicle.
In a nutshell, the crankshaft and rod bearings are two parts of the larger mechanical system within the internal combustion engine.
How Rod Bearings Influence Engine Performance
Rod bearings have a direct impact on an engine’s performance. When operating correctly, they ensure that the engine runs smoothly by reducing friction and wear. They do this by maintaining a thin film of oil between the crankshaft and the bearing itself, minimizing direct metal-to-metal contact.
Symptoms of a failing rod bearing might include knocking noises, reduced engine power, increased oil consumption, or even complete engine failure in severe cases.
Therefore, maintaining healthy rod bearings is critical to sustaining the optimal performance of an engine, highlighting their significance in the broader function of an internal combustion engine.
Identifying and Diagnosing Rod Bearing Issues
Just like any other mechanical component, rod bearings are subject to wear and tear and can eventually fail. Identifying and diagnosing these issues early can prevent further damage to the engine and avoid costly repairs.
Common Signs of Rod Bearing Failure
Understanding the common signs of rod bearing failure can help in early detection and timely repair. Some of the typical symptoms include:
- Engine Knocking Noises: This is often the first sign of a failing rod bearing. When the bearing starts to wear out, it can create a knocking or rumbling sound that becomes more noticeable as the engine speed increases.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A damaged rod bearing may cause the engine to lose power and performance. The vehicle might struggle to accelerate or maintain speed, particularly under heavy loads or high speeds.
- Increased Oil Consumption: If a rod bearing is failing, the engine may start to consume more oil than usual. This is because the damaged bearing can cause increased friction, leading to higher engine temperatures and more significant oil consumption.
- Metal Particles in the Oil: During routine oil changes, the presence of metal particles in the oil can indicate bearing wear. These particles can come from the bearing surface as it wears down and mixes with the engine oil.
Diagnostic Methods
Several diagnostic methods can confirm the presence of a rod bearing issue:
- Visual Inspection: Removing the oil pan and inspecting the rod bearings can often reveal signs of wear or damage.
- Oil Analysis: This involves testing the used engine oil for metal particles. High concentrations of certain metals can indicate a problem with the rod bearings.
- Mechanical Diagnosis: Mechanics may use specialized tools like a mechanic’s stethoscope to listen for abnormal noises that might indicate a bearing problem. They might also use engine scanning tools to check for any related diagnostic trouble codes.
Repair and Replacement of Rod Bearings
The condition of rod bearings is fundamental to the overall health and function of an engine. Recognizing when to replace them and understanding the replacement process is crucial for optimal engine performance.
When to Replace Rod Bearings
This can manifest as knocking or rumbling noises, increased oil consumption, reduced engine performance, or metal particles found in the engine oil.
However, certain factors can shorten their lifespan, such as poor maintenance, lack of lubrication, engine overheating, or the use of low-quality engine oil.
Replacement Process
Replacing rod bearings is a complex task typically performed by professional mechanics or individuals with advanced automotive knowledge and skills. The process involves:
- Engine Disassembly: To reach the rod bearings, it’s often necessary to partially or fully disassemble the engine, which can be a complex and time-consuming task.
- Old Bearing Removal: Once accessible, the old rod bearings are removed from the engine block. It’s important to inspect the crankshaft at this stage for any signs of wear or damage.
- New Bearing Installation: The new bearings are then carefully installed. This should be done with great care to avoid damaging the new bearings.
Costs and Considerations
The cost of replacing rod bearings can vary widely based on the make and model of the vehicle, the cost of the parts, and the complexity of the installation process. It’s a labor-intensive task and can therefore be quite costly in terms of labor charges.
If the engine has many miles on it and shows signs of extensive wear, a complete engine rebuild or replacement might be a more cost-effective and reliable solution in the long run.
By understanding these factors, you can make a well-informed decision about when and how to replace rod bearings, ultimately contributing to the longevity and performance of your engine.
Preventive Measures and Maintenance of Rod Bearings
Proper maintenance and preventive measures can significantly extend the lifespan of rod bearings and improve engine performance. They can also help avoid costly repairs and unwanted downtime.
Routine Checks
Routine checks are an essential part of any preventive maintenance plan for your vehicle. These checks can help detect any potential issues before they escalate into severe problems.
For rod bearings, routine checks can include:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes can prevent the buildup of dirt and other contaminants that can cause wear and tear on the rod bearings.
- Noise Monitoring: Regularly listening to your engine can help you detect unusual sounds, such as the knocking or rumbling noises that can indicate a failing rod bearing.
- Performance Monitoring: Keeping an eye on your vehicle’s performance can also help identify potential problems. A loss of power, increased oil consumption, or poor fuel efficiency can all be signs of a potential issue with the rod bearings.
Importance of Lubrication
Proper lubrication is crucial for the longevity and performance of rod bearings. The oil forms a protective barrier between the bearings and the crankshaft, reducing friction and preventing direct metal-to-metal contact.
It’s important to use high-quality engine oil and to change it at the recommended intervals. This helps ensure that the oil maintains its lubricating properties and doesn’t break down or become contaminated over time.
Low oil pressure can lead to insufficient lubrication of the bearings, which can cause them to wear out more quickly.
By implementing these preventive measures and maintenance tasks, you can help ensure the optimal function and longevity of your vehicle’s rod bearings.
