crankshaft position sensor which is typically at the bottom of the engine.
Common locations include near the front or rear crankshaft seal, on the engine block, or near the flywheel or harmonic balancer.

Introduction
What is the Crankshaft Position Sensor?
The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) is a crucial component within a vehicle’s engine. It plays a vital role in monitoring the engine’s many moving parts.
Characteristics of the Crankshaft Position Sensor
The CKP is usually located on the engine block, near the crankshaft. Based on the crankshaft’s position and speed, the CKP sends a signal to the fuel injection computer or the ignition control module, which in turn sends signals to other parts of the engine to time the ignition properly or control variable valve timing.
Importance of the Crankshaft Position Sensor in Vehicles
The Crankshaft Position Sensor is a pivotal component in modern vehicles. By determining the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft, the CKP helps the ECU manage the timing of fuel injection and ignition. This optimizes engine performance, ensuring smooth operation, efficient fuel usage, and reduced emissions.
The Role of the CKP in Vehicle Performance
If the CKP malfunctions, the vehicle may experience a range of issues such as poor fuel economy, engine misfires, or even failure to start. Therefore, understanding the location, function, and signs of a faulty CKP is of utmost importance to vehicle owners and mechanics.
Understanding the Car Engine
Basic Engine Components
An internal combustion engine, the most common type of engine in vehicles, comprises several key components. Each of these parts plays a critical role in the functioning and efficiency of the engine.
Main Components of an Internal Combustion Engine
- Cylinder: The core part of an engine where the combustion of fuel occurs. The number of cylinders in an engine determines its power output. More about cylinders can be found in this Wikipedia article.
- Piston: A cylindrical piece of metal that moves up and down inside the cylinder.
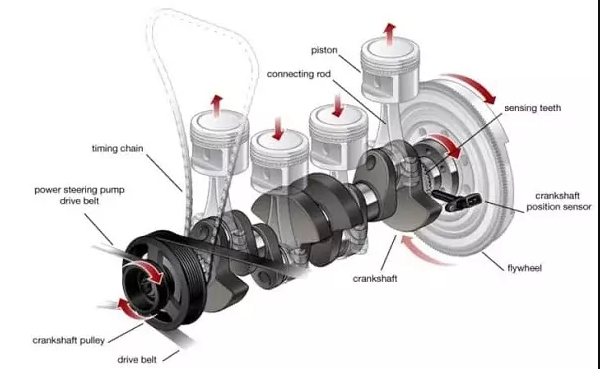
- Crankshaft: Converts the up and down motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Connecting Rod: Connects the piston to the crankshaft and transmits the power from the piston to the crankshaft.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinder.
- Valves: Controls the intake of air-fuel mixture and the expulsion of combustion gases.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of valves.
Role of the Crankshaft in an Engine
The crankshaft is one of the primary components of an engine and plays a vital role in converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. This rotation then drives the vehicle’s wheels.
Importance of the Crankshaft in Power Transmission
In addition to this, the crankshaft drives other components such as the alternator, water pump, and oil pump, contributing to the overall functionality of the vehicle.
The design and functionality of crankshafts can vary between different types of engines.
Location of the Crankshaft Position Sensor
General Location of Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) is usually found in close proximity to the engine’s crankshaft. The precise location of the CKP can vary significantly depending on the make and model of the vehicle, but it is often found either on the crankshaft pulley, the flywheel, or the camshaft.
Identifying the Crankshaft Position Sensor
The CKP is typically a two or three-wire sensor that is cylindrical in shape. Its housing is often made of plastic or metal, and it usually features a plug or connector for its electrical connection. This sensor is engineered to withstand harsh engine conditions and is generally bolted by one or two bolts to the engine block, transmission bell housing or engine cylinder head. More detailed information can be found in this Wikipedia article.

Variations in Position Sensor Location Across Different Vehicles
Due to the differing designs and configurations of different vehicle makes and models, the location of the CKP can vary.
Common CKP Locations in Various Car Models
For example, in many Ford vehicles, the sensor is located at the front of the engine, near the crankshaft pulley. In contrast, some Chevrolet models have the CKP located at the back of the engine, near the transmission bell housing. Some BMWs have the sensor located on the front of the engine, integrated into the engine timing cover.
Identifying the Crankshaft Position Sensor
Physical Characteristics of a Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) is typically a small, slim device that is usually cylindrical in shape. It often features a plastic or metal housing to protect the sensor element and electronics. This housing also provides a mounting point for securing the sensor to the engine or transmission.
Details of the Crankshaft Position Sensor
On one end of the sensor, you might notice a detection element. This is the part of the sensor that reads the crankshaft’s position and speed. For more details about the physical characteristics of a CKP, refer to this Wikipedia article.
Tools Needed for Locating the Crankshaft Position Sensor
Locating the CKP requires certain tools that aid in both identifying and accessing the sensor.
List of Necessary Tools
- Vehicle Service Manual: The manual usually provides a detailed diagram of the engine, which can help locate the CKP.
- Inspection Light: A good light source is essential when inspecting the engine, especially when the CKP is located in a hard-to-reach area.
- Mirror on a Stick: This tool can be beneficial when the CKP is located in a spot that is difficult to see directly.
- Socket Set: This may be needed to remove any parts that obstruct the view or access to the CKP.
These tools should help most individuals locate the CKP, but in some cases, professional assistance might be necessary.
Signs of a Faulty Crankshaft Position Sensor
Symptoms of a Bad or Failing Crankshaft Position Sensor
A faulty crankshaft position sensor can cause several problems, given its pivotal role in the engine’s operation. It’s crucial to be aware of these symptoms to address potential issues promptly.
Common Indicators of a Malfunctioning CKP
- Engine Misfires or Stalling: This can occur if the faulty CKP provides incorrect data to the ECU, leading to incorrect fuel delivery and ignition timing.
- Difficulty Starting the Vehicle: If the CKP is malfunctioning, the ECU may not receive the necessary information to initiate the ignition process.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty CKP can trigger the check engine light to come on, indicating that the vehicle needs servicing.
- Irregular Engine Performance: Inconsistent acceleration, reduced fuel efficiency, or unusual engine noise can be a symptom of a bad CKP.

How a Faulty Crankshaft Position Sensor Affects Car Performance
A malfunctioning CKP can have significant negative impacts on the performance of a vehicle due to its role in various essential engine operations.
Effects on Vehicle Operations
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: Incorrect data from the CKP can lead the ECU to adjust fuel delivery incorrectly, which can result in poor fuel efficiency.
- Reduced Engine Performance: Engine power and responsiveness may be compromised if the CKP is not functioning correctly.
- Potential Engine Damage: Prolonged driving with a faulty CKP may lead to other engine problems, such as damage to the catalytic converter due to improper fuel burning.
The impact of a faulty crankshaft position sensor on vehicle performance underscores the importance of prompt maintenance and replacement when necessary.
Testing and Replacing the Crankshaft Position Sensor
Step-by-step Guide to Test a Crankshaft Position Sensor
Testing a Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) requires a step-by-step approach to ensure accurate diagnosis.
Testing Process for CKP
- Access the CKP: Refer to your vehicle’s service manual to locate the CKP.
- Disconnect and Inspect the CKP: Unplug the sensor and check for any visible damage or wear.
- Test the CKP with a Multimeter: Set your multimeter to the Ohms setting to measure resistance.If the readings do not match the specified values, the sensor may be faulty.
- Reconnect the Sensor and Test Drive: If the sensor passes the resistance test, reconnect it and take the vehicle for a test drive to see if any symptoms persist.
It’s worth noting that testing the CKP requires technical know-how and the right tools, so professional assistance may be necessary.
How to Replace a Faulty Crankshaft Position Sensor
Replacing a faulty CKP involves a series of steps.
Replacement Process for CKP
- Locate the CKP: The exact location of the CKP varies between vehicles. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for precise information.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Once located, disconnect the sensor plug, and then unbolt and remove the old sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor by bolting it in place where the old one was removed and then reconnect the sensor plug.
- Test the New Sensor: Start the engine and observe for any persisting symptoms.
Always remember to disconnect the vehicle battery before attempting to replace the CKP. You can find more information on how to replace a CKP in this Wikipedia article.
Preventive Maintenance for Crankshaft Position Sensors
Regular Check-ups and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and check-ups can help extend the lifespan of a Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) and ensure that it functions optimally.
Importance of Routine CKP Inspections
This involves visually inspecting the CKP for any obvious damage, as well as checking the connector and wiring for any signs of corrosion or wear. A professional mechanic can also perform a diagnostic test to ensure the sensor is operating correctly.
Moreover, clean the area around the CKP during maintenance to prevent dust or debris build-up, which could interfere with the sensor’s operation. Learn more about routine automotive check-ups in this Wikipedia article.
Best Practices for Prolonging Sensor Life
Proper care and attention can significantly prolong the life of your CKP.
Tips for Extending CKP Lifespan
- Avoid Overheating: High engine temperatures can damage the CKP. Regularly check your cooling system to ensure it’s working effectively.
- Keep the CKP Clean: Regularly clean the area around the CKP to prevent dust or debris from entering the sensor.
- Regular Servicing: Regular vehicle servicing ensures any potential issues are identified and resolved early, reducing the risk of damage to components like the CKP.
By following these practices, you can ensure that the CKP and other engine components function correctly and last as long as possible. For more details on extending the life of vehicle components, you can refer to this Wikipedia article.
Conclusion
Recap on the Importance and Location of the Crankshaft Position Sensor
The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP) is a critical component of a vehicle’s engine. Its primary role is to monitor the speed and position of the crankshaft, providing essential data to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
Key Takeaways about CKP
As we’ve covered, the CKP’s location varies across different vehicles, but it’s generally found near the crankshaft. Brands like FEDA take great care in the placement and protection of this essential sensor. Being able to identify and locate the CKP is a vital skill for any car owner or mechanic.
Final Thoughts and Advice for Car Owners
Proper maintenance and understanding of your vehicle’s components, like the CKP, can save you from expensive repairs and ensure your car runs efficiently.
Advice to Vehicle Owners
For FEDA and other brands’ vehicles, always refer to your service manual for specific information on part locations and maintenance schedules. If you’re unsure, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Regular check-ups, proper cleaning, and preventive maintenance are crucial in extending the life of the CKP and your vehicle as a whole. Find more helpful tips on car maintenance in this Wikipedia article.
Referensi
- Crankshaft Position Sensor – Wikipedia
- Auto Mechanic – Wikipedia
- Automotive Technician – Wikipedia
- Auto Maintenance – Wikipedia
