A deep dive into the complex world of internal combustion engines invariably leads us to the connecting rod. Often abbreviated as “conrod,” this critical component forms the heart of the engine, establishing the vital link between the piston and the crankshaft. Understanding the different parts of a connecting rod, their functions, and their impact on engine performance can provide fascinating insights into automotive engineering.
The primary component of the connecting rod is the rod itself, often referred to as the rod beam. This central piece needs to be robust, designed to bear the brunt of the engine’s tensile and compressive forces during operation. In essence, the rod beam forms the backbone of the connecting rod, providing structural integrity and resilience.
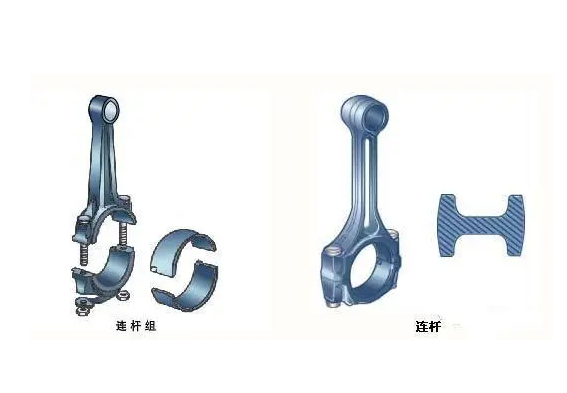
On either end of the connecting rod, you’ll find the small end and the big end. The small end, as its name suggests, is the thinner end, designed to connect to the piston through the piston pin. The big end, conversely, is broader and connects to the crankshaft at the crankpin. The big end usually adopts a split design, facilitating assembly and disassembly around the crankpin.
Bushings, commonly made of bronze, are often incorporated at both ends of the connecting rod. These bushings significantly reduce friction and wear during engine operation, contributing to the component’s longevity.
Yet another crucial part of the connecting rod is the bearing shells. Located in the big end of the connecting rod, these shells boast excellent anti-friction properties, reducing friction between the connecting rod and the crankpin.
Securing the big end around the crankpin are the bolts and nuts. These components, while small, are engineered to withstand the high stresses and strains experienced during engine operation.
Lubrication ports also play a vital role in the smooth operation of the connecting rod. These channels allow oil to flow to the critical areas of the connecting rod, reducing friction and heat, thereby extending the life of the component.
The connecting rod cap and cap screws form part of the big end that encloses the crankpin. The cap is typically bolted to the connecting rod body using the cap screws, designed to withstand high forces and temperatures. In essence, the rod cap and screws help maintain the structural integrity of the connecting rod during engine operation.
Dowel pins are essential in maintaining the alignment of the connecting rod. They ensure that the cap and rod body align correctly during assembly, maintaining balance and stability.
The junction where the rod body and cap meet is known as the parting line. The parting line is critical for maintaining the alignment and balance of the connecting rod, enabling smooth and efficient engine operation.
A multitude of factors, including the length and weight of the connecting rod, the beam design, and the choice of materials, impact the design of a connecting rod. Balancing these factors is key to optimizing engine performance and efficiency.
Advancements in technology have led to improvements in conrod design and manufacturing techniques. Innovations such as heat treatment processes, surface coatings, and strict inspection protocols have ensured the production of durable and reliable connecting rods.
Regular maintenance and replacement of worn-out parts are essential for the longevity and performance of connecting rods. Finally, as we look towards the future, we can anticipate continuous improvements in the design, materials, and manufacturing processes of connecting rod parts. These advancements will contribute to more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly engines, keeping pace with the ever-evolving demands of the automotive industry.
Introduction
This section introduces the role of connecting rods in internal combustion engines and sets the stage for the detailed discussion that follows.
The Rod Beam
This part of the article delves into the robustness of the rod beam, its function, and its importance in withstanding the tensile and compressive forces during engine operation.

The Small End and Big End
Here, the article explains the roles of the small and big ends of the connecting rod, their design, and how they facilitate the assembly and disassembly of the engine.
The Role of Bushings
This section explains the importance of bushings, typically made of bronze, in reducing friction and wear during engine operation.
The Function of Bearing Shells
This part of the article highlights the role of bearing shells in the big end of the connecting rod, emphasizing their anti-friction properties and their contribution to reducing friction between the connecting rod and the crankpin.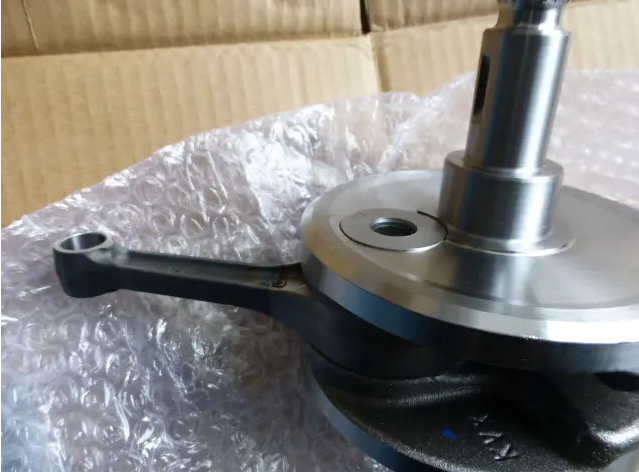
The Importance of Bolts and Nuts
This section discusses the crucial role of bolts and nuts in securing the big end of the connecting rod around the crankpin and their ability to withstand high stresses and strains during engine operation.
The Role of Lubrication Ports
This part of the article explains the vital role of lubrication ports in enabling oil flow to critical areas of the connecting rod, thereby reducing friction, heat, and extending the component’s life.
The Connecting Rod Cap and Cap Screws
This section highlights the role of the connecting rod cap and cap screws in maintaining the structural integrity of the connecting rod during engine operation.
The Significance of Dowel Pins
Here, the article discusses the critical role of dowel pins in maintaining the alignment of the connecting rod during assembly, thereby ensuring balance and stability.
Understanding the Parting Line
This section discusses the role of the parting line in maintaining the alignment and balance of the connecting rod, thus enabling smooth and efficient engine operation.
Factors Impacting Conrod Design
In this part, the article discusses various factors that impact the design of a connecting rod, including its length and weight, beam design, and choice of materials.
Length and Weight
This subsection focuses on how the length and weight of the connecting rod impact its design and function.
Beam Design
This part delves into the role of beam design in connecting rod functionality.
Material Selection
Here, the text discusses how the choice of materials for the connecting rod can affect its performance.
Technological Advancements in Conrod Design
This section discusses the role of technological advancements, such as heat treatment processes, surface coatings, and inspection protocols, in improving conrod design and manufacturing.
The Importance of Maintenance and Replacement
Here, the article emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance and replacement of worn-out parts for the longevity and performance of connecting rods.
Future Trends in Conrod Design
This section gives readers a glimpse into the future of conrod design, including anticipated improvements in design, materials, and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
This part wraps up the article, summarizing the key points discussed and emphasizing the importance of connecting rod parts in the overall performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines.
